Can phytogenics address aquaculture challenges?
As in other production sectors, optimizing fish and shrimp production performance is crucial to the success of the aquaculture sector. Efficient feed management, including optimized feed formulation, together with proper health and welfare management determines higher production output and helps to address aquaculture challenges.
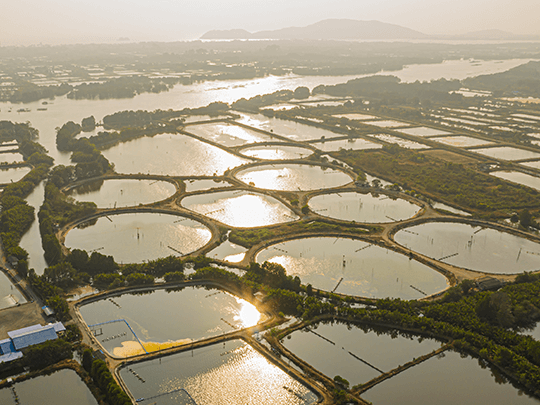

As part of a proactive approach to higher production performance and healthier fish and shrimp, the use of functional and sustainable additives, such as phytogenics, has demonstrated to be an effective tool to boost fish and shrimp performance and consequently, better profitability of aquaculture production.
Did you know?
Global fish consumption has been growing at an annual rate of 3.1% from 1961 to 2017? It’s accounting for almost 20% of the protein of animal origin consumed worldwide. In 2018, aquaculture contributes for approximately 46% of global fish production (FAO, 2020).
Performance in aquaculture faces many challenges
The mucosal tissues of fish and shrimp, including the gut, are exposed to a variety of biological, physical and chemical hazards. These environmental hazards include potential pathogens, stress conditions and changes in the rearing environment like water temperature and salinity. The consequence of prolonged exposure to some of them is often impairment of tissue integrity and physiological functions, which may directly reduce the profitability of aquaculture production. On top of that, constantly rising raw material prices, limited availability, and the need for sustainable fish feed production with sustainable feed ingredients increase the pressure on feed nutritionists who must find alternative raw materials without compromising animal growth performance and health. They must look for alternative strategies to support the efficiency and profitability of aquaculture production.
Unfortunately, the search for alternative sources of raw materials is not an easy task.
On the one hand, replacing marine raw materials such as fishmeal or fish oil with single or combined vegetable proteins and oils can be a suitable alternative - whether for economic or sustainability reasons. On the other hand, this can also lead to inefficient and uneconomic production, as there is a lack of essential nutrients for optimal growth performance and welfare, as well as potential antinutritional factors.
In addition...
...depending on the species and the replacement level, plant-based raw materials can have undesirable effects on the health and functionality of the intestinal mucosa of fish and shrimp. This may result in impaired nutrient uptake and in higher susceptibility to disease outbreaks. In addition, the presence of undigested nitrogenous compounds can promote the formation of ammonia by intestinal microbiota, resulting in poor water quality. Consequently, growth performance, feed efficiency and survival will be affected.

Performing nature for performing aquaculture
Phytogenic feed additives (PFAs), commonly defined as plant-based feed additives or botanicals, represent a group of natural substances used in animal nutrition. These substances are derived from herbs, spices, other plants and their extracts consisting of highly active plant substances. Phytogenics encompass much more than essential oils: they include spices or bitter substances, saponins, flavonoids, mucilages or tannins. During the last two decades, research on phytogenics as potential functional ingredients in animal production has increased and with it their commercial use in all areas of animal production.
Phytogenics can act as natural growth promoters that improve the palatability of feed, stimulate appetite, increase nutrient uptake and thus support growth performance in animal species – making them a valuable tool in terms of reducing the use of antibiotic growth promoters animal production. The broad spectrum of phytogenics’ mode of action provides a competitive advantage in addressing the most pressing challenges in fish and shrimp production.

Several studies demonstrated that phytogenics stimulate the secretion of digestive enzymes, contribute to maintain gut mucosa structure, support a healthy microbiome, and reduce stress. All in all, supporting growth performance and feed efficiency by supplementing phytogenics, the production cycle may be shortened, resulting in profitable aquaculture production and economic benefits for the farmer.

Find out more about aqua solutions

Alex Makol
Dr. Alex Makol has a strong background in fish nutrition. After studying Marine Biology in Fairleigh Dickinson University (FDU) in New Jersey (USA), he continued developing his scientific background with a Master in Aquaculture Fish Nutrition and completed his scientific background with a PhD in Aquaculture Fish Nutrition in the University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria (ULPGC), in Spain. Alex joined to Delacon 4 years ago where he is responsible as Global Unit Manager Aqua to develop the Aquaculture line products.










