Fenugreek – a versatile plant in animal feed (part 2)
In the first part of our fenugreek series you discovered the amazing history of this versatile medical plant. In this part you can learn about the active ingredients of fenugreek seeds….

While we have dealt with the history and botanical characteristics of fenugreek in the first part of our series, we now dive deeper into the active ingredients of the seeds of this special plant.
Do you know the main components in fenugreek seeds?
Discover more in this article and inform about the specifities of the main components with a special view on mucilages.
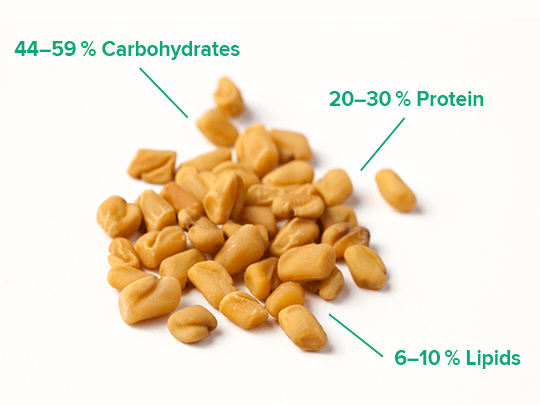
Fenugreek seeds have a high content of various minerals: calcium, zinc, phosphorus, manganese and iron are present in high concentrations compared to other legumes. The seeds are also rich in saponins, flavonoids, carotenoids and coumarins.
Content of dried fenugreek seeds (according to Basu and Srichamroen, 2010)
According to Basu and Srichamroen (2010), fenugreek seeds contain three active components which are responsible for its health-promoting effect: galactomannans, saponins and 4-hydroxy-isoleucine. Here we would like to introduce you to these main components in fenugreek:
Galactomannans
Galactomannans are polysaccharides which consist of galactose and mannose. These polysaccharides are abundant in the cell walls of the endosperm of legume seeds. Galactomannans differ in their ratio of galactose to mannose depending on the plant of origin. The structural properties of fenugreek galactomannans enable them to increase digesta viscosity in the intestine – this is why they are also called mucilages.
Saponins
Saponins are particularly abundant in legumes – but are also found in numerous other plants, e.g. in the so-called soap tree Quillaja saponaria. Saponins can be very different in their structure, but they have one thing in common: they have a sugar residue which is linked to a triterpenoid or steroid part. In fenugreek, the sugar residue is connected to the steroid part. The saponins in fenugreek therefore belong to the steroidal saponins.
4-hydroxy-Isoleucine
(4-OH-Ile)-hydroxy-isoleucine is a polar non-protein amino acid that occurs exclusively in some selected plants, especially in Trigonella species. In fenugreek seeds the amino acid is present as a diastereoisomer (Basu and Srichamroen 2010).
References upon request

Did you know?
Mucilages in animal feed can be used to protect the intestinal mucosa. According to Chowdhury et al (2017), mucilages can stimulate mucus secretion of the superficial epithelial cells and thus act against ulcer triggers.
Mucilages also help to relieve constipation by increasing peristalsis in the gastrointestinal tract and facilitating bowel evacuation (Wani and Kumar, 2018). In addition, certain mucilages have a prebiotic effect. The intestinal microbiota can break down the polysaccharides into short-chain fatty acids that serve as energy suppliers (Majeed et al., 2018).
| Effect | Reference | |
| Saponins |
– Hypocholesterolemic – Inhibition of inflammatory cytokine production in THP-1 cells and melanogenesis in B16F1 cells – Antifungal – Improvement of adipocyte differentiation and inhibition of inflammation in fatty tissue – Hemolytic |
Basu and Srichamroen, 2010 Kawabata et al., 2011 Sauvaire et al., 2010 Uemura et al., 2010 Elmadfa and Kroken, 1980 |
| Galactomannans |
– Increase of intestinal digestive enzymes in rats with diabetes – Increase of the phagocytosis rate of peritoneal macrophages – Hypoglycemic |
Hamden et al., 2010 Ramesh et al., 2002 Basu and Srichamroen, 2010 |
| 4-Hydrocy-Isoleucin | – Stimulation of insulin secretion | Basu and Srichamroen, 2010 |
Do you want the entire article as PDF including all references?

You are only one click away.

Anne Oberdorf
Anne has always been fascinated by the unknown, the diversity and beauty of nature. Her love for nature brought her to Delacon in 2018 after studying agricultural sciences, where she worked as Technical Communications Manager and later as Product Manager Aquaculture. Since February 2021, she has been taking a new, natural career path outside of Delacon.










